Health agencies warn that measles still challenge Europe, despite a decline in cases in 2025 after a record year. Experts urge governments and communities to act fast to stop vaccination hesitancy and prevent new outbreaks across the region.
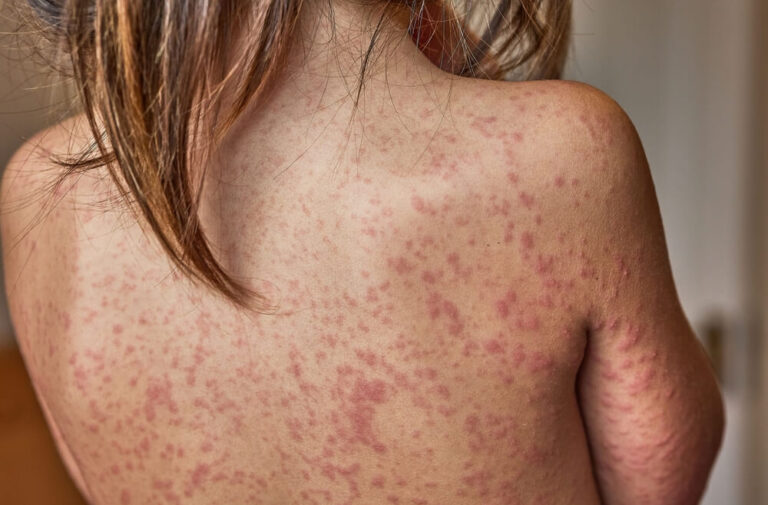
Measles often disappear from public debate, but they continue to spread across Europe. In 2024, Europe reported 127,350 measles cases, which marked the highest figure since 1997. Cases dropped in 2025, but infections still doubled compared with 2023, according to the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control.
Sabrina Bacci, head of the ECDC programme on vaccine-preventable diseases and immunisation, said Europe should lead the world in measles elimination. She said Europe has a safe and highly effective vaccine, strong knowledge, sufficient resources, and some of the most robust surveillance tools to control this preventable disease.
Vaccination Targets Remain Unmet Across the Continent
Experts say at least 95 percent of eligible people must receive two vaccine doses to prevent outbreaks and protect vulnerable groups. These groups include children too young to receive vaccines and people who cannot be vaccinated for medical reasons.
The ECDC reported that 8 in 10 people who fell ill with measles in 2025 had not been vaccinated. This trend mirrored the pattern seen in 2024 and exposed persistent gaps in immunisation coverage.
Bacci said individual vaccination protects others who cannot be vaccinated by reducing virus transmission. She said vaccination represents self-protection and solidarity. She added that eliminating measles remains achievable if societies act together.
A Highly Contagious Virus With Severe Long-Term Effects
Measles rank among the most contagious viruses affecting humans. One infected person can transmit the virus to up to 18 unvaccinated people, which makes it far more contagious than influenza.
The disease can cause long-term and debilitating health complications. Measles can damage the immune system by erasing its memory of how to fight infections for months or even years. The World Health Organization warns that survivors become vulnerable to other diseases and death after infection.
Vaccination Remains the Only Effective Protection
There is no cure and no specific treatment for measles. The illness usually lasts about two weeks without complications, but vaccination remains the key tool to stop transmission and prevent severe outcomes.
Regina De Dominicis, regional director for Europe and Central Asia at UNICEF, said declining case numbers do not remove the conditions that caused the recent resurgence. She stressed the urgent need to counter vaccine hesitancy and misinformation. She warned that children will remain at risk of death or serious illness without higher vaccination coverage.
Hans Kluge, the WHO regional director for Europe, urged people to rely only on verified health information from trusted sources. He warned about widespread misinformation and said eliminating measles is essential for national and regional health security.
Rising Measles Cases Threaten Global Progress
Europe does not stand alone in facing rising measles cases. After years of progress in global measles control, the disease has steadily increased in recent years.
The WHO announced earlier this year that Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Spain, the United Kingdom, and Uzbekistan lost their measles-free status after the surge in cases in 2024. A country loses this status when the virus returns and transmission continues for more than one year.